Contents
NBFC or Non-Banking Financial Companies have played play a crucial role in promoting inclusive growth in India, so far. By catering to the diverse financial needs of those falling outside the purview of banks.
NBFC Companies are financial intermediaries involved in the business of accepting deposits, delivering finances. They channelize scarce financial resources towards the formation of capital.
However, they do not include services related to agriculture activity, industrial activity, sale, purchase or construction of immovable property.

NBFCs provide funds to businesses involved in transportation, wealth creation, employment generation, bank credit in rural segments, and support financially weaker sections of the society. Emergency services such as financial guidance and assistance are also provided to the clients about insurance, etc. All these activities made the NBFC role an indispensable one in the development of our economy.
NBFC Companies often take the lead by providing innovative customized financing solutions to MSMEs (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises) that suit their requirements better. Though they are different from banks, they serve to supplement the role of the banking sector in meeting the ever-increasing financial needs of the business sector, providing credit to the unorganized sector and small local borrowers. Because they provide financial services, Companies also have to get NBFC License by the Reserve Bank of India, RBI.
Principal Business for NBFC Companies
One aspect not to be missed is that the financial activity of loans/advances should be for activities other than its own. Else, all companies would have been NBFCs.
The term “Principal Business” is not defined by RBI, but only explained as that if the companies are engaged in agricultural operations, industrial activity, purchase and sale of goods, providing services or purchase, sale or construction of immovable property as their principal business and are doing some financial business in a small way, they will not be regulated by RBI. The Bank has defined it for the understanding of the term so that only companies predominantly engaged in financial activity get registered, are regulated, and supervised by it. This test is popularly known as a 50-50 test and is undertaken to ascertain whether or not a company is into financial business.

Even though RBI has given a numerical dimension to determine the principality of business. So, to identify a particular company as an NBFC, both the assets and the income pattern as evidenced by the last audited balance sheet of the company will be considered to decide its principal business. Both the criteria are required to be satisfied simultaneously to know its principal business.
For companies exclusively engaged in financial activity, the nature of “principal business” is obvious. But where a company carries on multiple businesses, of both financial and non-financial nature, and in different proportions, then how should one know?
The RBI Act has defined “principal business” by way of exclusion. Accordingly, all non-banking companies carrying on some sort of financial business are NBFCs except when carrying on any non-financial business as a principal business.
Financial Activities
Financial activity as the principal business is when the financial assets of the company constitute more than 50% of the total assets. And income from financial assets makes up for more than 50% of the gross income. The company which fulfills both these requirements will be granted NBFC registration by RBI.
Now, under the Companies Act, Section 372A, an investment company has been defined in a similar way. As a company whose principal business is the acquisition of shares, debentures, stock, or other securities. No criteria have been laid down in the Act for determining the term “principal business”. However, judicial pronouncements have emphasized that “principal business” cannot be quantified in absolute terms using the figures stated in the financial statement of a company (say Balance sheet). It is more the intention of the party that matters. Whether it intends to carry on a business activity as its primary activity.
Financial Assets
As per AS 26, Financial Asset includes all deposits and investments in Shares, Debentures, etc. They include:
- Cash,
- Stocks and equity instruments of another entity,
- Contractual claim to receive cash or other financial assets from another entity,
- Contractual claim to exchange financial instruments with another entity under conditions that are potentially favorable,
- A contract that will or may be settled in the company‘s own equity instruments, and is:
- An ownership interest in another company:
- a non-derivative for which the company is or may be obliged to receive a variable number of the entity’s own stock instruments, or
- a derivative that will or may be settled other than by the exchange of a fixed amount of cash or another financial asset for a fixed number of the company’s own equity instruments.
Fixed Deposits with Banks as Financial Assets
Moreover, any investments in FDs (fixed deposits) are not to be treated as financial assets. And the interest income on FDs with banks is not to be treated as income from financial assets. Because these are not covered under the activities mentioned in the definition of “Financial Institution” in Section 45I(c) of the RBI Act, 1934. The clarification is that FDs constitute near money and are used only for temporary parking of idle funds, and/or in the above cases, till the commencement of NBFC business.
Thus, these investments by NBFC Companies do not amount to carrying the business of finances.
Also, note that only FDs with banks have been excluded and no other similar liquid assets.
NOF of NBFC Companies
NOF or Net Owned Fund has been defined by RBI as:
- The paid-up equity share capital and free reserves as per the latest balance sheet of the company is included, after deducting the following:
- Accumulated losses,
- Deferred Revenue Payments,
- Other intangible assets.
Further, below gets deducted:
- Investment of such companies in the share of its subsidiaries, same group companies, and other NBFC Companies,
- Book value of the debentures/bonds/outstanding loans and advances (including lease finance and hire purchase) made to, and deposits with its subsidiaries or companies within the same group more than 10% of the amount calculated as above.
Hope we have been able to make these terms, that have been vaguely defined by RBI, easily understandable for you!
NBFC License India is dedicated towards simplifying the complex world of NBFC.
We are a leading online platform for NBFC Registration, to buy NBFC or NBFC Sale India. We also aid in mergers and collaborations.
For more information on the subject, you can call us at (+91) 8750008585.
Related Articles:
What is NBFC Working in its Full Form
NBFC Guidelines: Registration, Compliances, Returns & Prudential Norms
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is an NBFC?
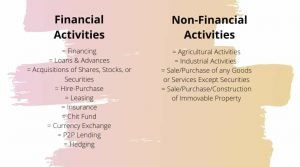
An NBFC or Non-Banking Financial Company is a company registered under the Companies Act involved in the business of financial activities such as –
- loans and advances
- acquisition of shares/stocks/bonds/debentures/securities issued by Government or local authority or other marketable securities of similar nature
- chit fund
- hire-purchase
- leasing
- insurance
It doesn’t include those organizations whose principal business is of
- industrial activity
- agriculture activity
- Purchase or sale of goods other than securities or construction/sale/purchase of immovable property.
Also, the principal business of NBFCs must be of receiving deposits under an arrangement or any scheme in instalments or lump sum by the way of contributions or in any other manner.
Q. Who can get NBFC License?
- A company desiring of commencing the business of non-banking financial institution as defined under Section 45 I (a) of the RBI Act, 1934 should comply with the following:
- it should be a company registered under Section 3 of the Companies Act, 1956
- It should have a minimum net owned fund of Rs. 2 crore. (The minimum net owned fund (NOF) required for specialized NBFCs like Micro Finance Institutions, Factors, Core Investment Companies, etc.
Q. What is the process of NBFC Registration?
- An application is submitted online along with the required documents. And a CARN (Company Application Reference Number) is generated. This reference number is to be used for all future communications and inquiries.
- The hard copy of the Application and the accompanying documents are sent to the Regional Office of the RBI.
- The regional office, after checking the documents, sends them to the central office of the RBI. There, the application is examined thoroughly and a background check is conducted.
- If the company is complying with all the terms and conditions u/s 45-I A of the RBI Act, the NBFC License and CoR is granted to the applicant.
Q. What documents are required for NBFC registration?
- Main documents to be attached to the application for NBFC registration are:
- Certificate of Company Incorporation
- Company’s Bank Account with a minimum paid-up equity share capital of Rs. 2 crore
- MoA & AoA
- Address proof of the company
- Duly filled up and signed Annexure I, II, and III
- Detailed information about the Directors
- Document of administration and management of the company
- Audited financial accounts for the past 3 years
- Board resolution favouring NBFC registration
- A brief documentary about the company’s works and activities in past 3 years
- Income tax, PAN, etc.
- Any other relevant documents.
Q. What are the types of NBFCs in India?
The NBFCs can be categorized based on their activities, as:
- Asset Finance Company
- Investment Company
- Loan Company
- Infrastructure Finance Company
- Core Investment Company
- Micro Finance Company
- Mortgage Guarantee Company
- Housing Finance Company
Based on the deposits that they can hold, NBFCs can be classified into:
- Deposit accepting NBFCs
- Non-Deposit accepting NBFCs
They can be categorized as per their size, as:
- Systematically Important NBFCs
- Non-Deposit Holding NBFCs
Q. What is RNBC?
RNBC or Residuary Non-Banking Company is a class of NBFC which is a company and has as its principal business the receiving of deposits, under any scheme or arrangement or in any other manner. It doesn’t include Investment, Asset Financing, Loan Company. These NBFC companies must maintain investments as required by RBI, in addition to liquid assets. Their functioning is different from those of NBFCs in terms of method of mobilization of deposits and requirement of deployment of depositors’ funds as per Directions. Prudential Norms Directions are applicable to these companies also.

